Innovation and quality are some of the most important elements of the RECASENS Philosophy. All company processes revolve around our philosophy in order to ensure full customer satisfaction.
In our operating sector (Sunscreen, Textile Architecture, Technical Fabrics, Decoration, Marine and Transportation), investment in R&D+i is a constant. We are always working to improve fabric performance, optimize production processes both in quality and efficiency, and to respond to specific requests from customers.
RECASENS constantly works on developing new fabrics. The Marketing Department, along with R&D+i, continuously analyzes the trends and market requirements in the industry, enhancing existing products, and even creating new products for its customers, offering innovative and value-added solutions.
As part of these new innovative solutions, RECASENS has developed the Infinity Process for Recacril® and Recsystem® fabrics, a process in which materials are subjected to a high-tech treatment to ensure the durability of fabrics. In this process, nanoparticles from completely finished products cover the surface of the fabric fibers, forming a permanent coating. After treatment, the exposed surface and internal fibers are permanently protected from dirt accumulation and adverse effects of a wide range of atmospheric agents.
With low reactivity and high stability, the Infinity Process delivers lasting protection, especially against mildew, and provides excellent water-and-oil proofing, protecting awnings from both sun and water.
Quality
Our commitment to customer service, technical knowledge and quality has driven RECASENS to adopt a management system in compliance with ISO 9001:2008 certification, issued by TÜV Rheinland, and the implementation of a rigorous Quality Policy based on the following premises:
- Ensuring complete customer satisfaction through products tailored to our customers’ needs and requirements.
- Working for continuous improvement in our processes, products, services and training of our staff.
- Committing adequate resources to meet agreed commitments.
- Providing quality in manufactured products and services as the basis for the future of our company.
- Promoting the involvement and commitment of staff.
- Not providing products and services that break the applicable law, and being committed firmly with sustainable development and concerned with environmental challenges.
- Addressing deficiencies the moment they are detected.
- Optimizing and maintaining an appropriate working environment.
- Continually striving to set the optimal criteria for health and safety policy.
- The commitment of the Managing Director to fulfill these premises.
Warranty
The high quality of the raw materials used and stringent quality control procedures to which RECASENS fabrics are subjected throughout the production process allows us to offer a 5-year warranty on all products except Recacril® and RecScreen®, which have a 10-year warranty.
This warranty covers the deterioration of the canvas due to rot, mildew, and fading in regular atmospheric conditions. This warranty does not cover damage due to abuse, neglect, vandalism, perforations, burns and natural disasters. It also does not cover normal wear, soiling and stains from air pollution and environmental conditions.
The product must be properly installed and subjected to proper maintenance. The warranty, if applicable, does not cover assembly and manufacturing costs.
Certification
The use of high quality raw materials gives the canvas and technical fabrics from RECASENS an unbeatable performance of light fastness and weathering. In addition, acrylic, PVC and technical fabrics from RECASENS are recognized for their high mechanical abrasion resistance, tensile and tear, while resistant to molds, insects and putrefaction. This combination of features gives RECASENS fabrics the power to retain their strength and color for many years.

RECASENS canvases meet approval requirements according to European standard UNE-EN 13561:2004+A1:2009, but also some of its products have the following certifications:
OEKO-TEX® STANDARD 100

Due to the differences regarding legal requirements and safety concepts in different countries, and how the work is distributed internationally in the textile chain, you need a common security standard for harmful substances.
The Oeko-Tex® Standard 100 meets this need. It is a test certifying worldwide raw, intermediate and finished textile products at all stages of the process. Its aim is to ensure that textiles are free of harmful substances. The advantages Oeko-Tex® Standard 100 are:
- The production of textiles harmless from a human-ecological point of view.
- The streamlining and accelerating of supply relationships for producers and traders who wish to offer perfectly hygienic textile products to its customers.
- A reliable distinction of product for consumers who consciously favor hygienically harmless textiles.
UV STANDARD 801

The UV Standard 801 is a method of analysis to determine the Ultraviolet Protection Factor for awning fabrics, with consideration for how tissue tension, aging canvas by sunlight, rain and humidity might reduce the ability of the canvas to protect users. Consequently, these factors should be considered in the tests to give a reliable UPF for not endangering the user.
To ensure all these factors, the tests according to UV Standard 801 are performed under the following conditions:
- The measurements were made on wet and stretched canvas samples that have been previously subjected to artificial aging.
- Protection Factor is determined based on the maximum ultraviolet radiation and the most sensitive skin.
- The spectrum of solar radiation in summer in Australia, which contains more ultraviolet radiation than used by other standards (solar spectrum in Albuquerque, New Mexico, etc.) is simulated.
Due to the high level of exigency posed by the above conditions, RECASENS considers the UPF obtained by the UV Standard 801 as the most reliable to characterize our sunscreen canvases.
Sun Protection Concepts
Reflectance, transmittance and absorbance of solar radiation

When solar radiation hits any surface (glass, an awning, a curtain, etc.), it divides into three parts:
- REFLECTANCE – the energy reflected and dissipated by a surface;
- ABSORPTANCE – the energy absorbed and warmed by a surface;
- TRANSMITTANCE – the energy that passes through a surface and transmits through it
The amount of reflected, absorbed or transmitted solar radiation depends on the nature of the fabric. Each fabric behaves differently, depending on the following characteristics:
- Weight.
- Thickness.
- Color.
Effects of solar radiation
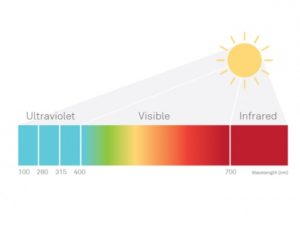
Solar radiation is electromagnetic radiation from the sun, part of which is absorbed by the atmosphere, while the other part reaches the surface of the earth.
The radiation reaching the surface is divided into three types:
- Ultraviolet (8% of total) is the most powerful energy and therefore most dangerous. Ultraviolet radiation is the main cause of skin lesions and is the major risk factor for most skin cancers.
- Visible Radiation (43%) has a wavelength between 360 nm (violet) and 760 nm (red), and is what produces glare.
- Infrared Radiation (49% of total) is less powerful, and produces warmth.
Thermal factors
To assess how a fabric performs we use the following factors:
- Solar Reflectance factor (Rs): Percentage of total incident solar radiation reflected by the fabric surface. The higher it is, the more energy is reflected by the fabric.
- Solar Absorptance factor (As): Percentage of total incident solar radiation that is absorbed by the fabric surface. The lower the factor, less fabric is heated.
- Solar Transmittance factor (Ts): Percentage of total incident solar radiation transmitted through the fabric. The lower it is, the lower the energy that passes through the fabric.
The sum of these three indices has a value of 100: Rs + As + Ts = 100%
Total Solar Factor (Gtot): The solar factor (TT/SF/g) of glazing is the percentage of the total solar radiant heat energy entering the room through the fabric and glass, taking into account both. The lower this factor, less solar radiation enters the building and therefore the fabric is more effective blocking solar radiation and reducing cooling requirements.
As already indicated above, the solar radiation absorbed by the fabric causes heating, which causes the fabric to become a heat emitter.
If the fabric is on the outside of the glass that encloses a room, the radiated heat is dissipated into the external environment. However, if the fabric is in front of the glass inside the room, the heat radiated by the fabric remains inside. Therefore, from the point of view of the thermal efficiency, it is more effective to place the fabric on the outside of the building.
Technically, this behavior is described by the value of the Exterior Solar Factor (if the fabric is on the outside) and Interior Solar Factor (if the fabric is inside).
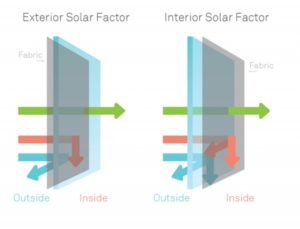
These four indices are called Thermal Indices as they are directly related to the thermal efficiency and thermal comfort provided by the fabrics.
Generally, the most used index in regulations and standards to specify the thermal efficiency of a fabric sunscreen is the Total Solar Factor (Gtot).
Optical indices
From the three components of solar radiation reaching the surface of the earth, visible radiation is the only one that has direct influence on visual comfort.
Visual comfort is the right combination of several factors: the nature of the (natural or artificial) light, its stability and its quantity relative to the visual demands of the activities to be performed, whether labor, domestic or rest. Inadequate correlation between lighting and activity lead to premature material fatigue, and in extreme cases, luminous imbalance.
To measure the ability of a specific fabric regarding the visible part of solar radiation, we use the following optical indices:
- Openness (Tvnn) or Openness Factor (OF): The percentage of the fabric surface occupied by holes. This index describes a feature of the fabric only and is independent of the color. The higher the degree of openness, the higher the amount of light will pass through the fabric. The lower the openness factor, the higher the amount of shade.
- Visible Light Transmittance (Tv): The total percentage of light radiated through the fabric.
- Visible Light Reflectance (Rvnh): The percentage of visible light radiation reflected by the fabric. When light passes through a fabric, the total transmitted light is spread in all directions (diffuse transmission). The diffusely transmitted light is softer, has less contrast, and generates lighter shades (smoother transition between light and shadow).
- Diffuse Light Transmission Factor (Tdif): The difference between the visible transmission factor and the openness factor: Tdif = Tv – OF.
- Tvndif refers to glare and shape recognition. A low value means greater visual comfort.
- Tvdifh refers to the lighting control, and is used to measure the diffusion capacity of a fabric. A high value indicates a greater contribution of natural light through fabric.
Regulation and legislation standards indicate Visible Light Transmittance factor (Tv) as the factor used to specify the visual comfort provided by a fabric.
The Solar Radiation and Banners
Installing a sun protection product, such as an awning or shade, allows control of the amount of sunlight and solar radiation entering a building through an opening. Depending on the type and color of the fabric selected, light contrast intensity is reduced, lowering the cooling requirements of the building.
For example, a dark colored fabric allows greater glare control by less light transmission, but the amount of reflected radiation is smaller than in a light color and the absorption percentage is greater. The solar radiation absorbed is transferred as heat, therefore, a dark fabric provides greater visual comfort but may reduce thermal comfort.
UV Protection Factor
Solar UV radiation is necessary for human health. For example, our body needs vitamin D, responsible for regulating bone calcium. This vitamin is formed by exposing skin to ultraviolet sun radiation. However, an excess of this radiation presents a significant risk of developing burns, and can even cause skin cancer.
There are different types of skin (up to 6 according to dermatologists). Each reacts differently when exposed to sunlight and has its own maximum exposure to sunlight to avoid damage. For example, Skin Type I can only be unprotected from sun exposure between 5 and 10 minutes before reddening.
The Ultraviolet Protection Factor UPF indicates how long a person can stay under the sun protection element without damaging the skin. A canvas with a UPF 50 allows a person with Skin Type I to be under it around 250 minutes.


